What Are The Best Investment Opportunities Right Now?
As we navigate through 2025, the investment landscape presents a myriad of opportunities across various sectors. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting, understanding these avenues can help you make informed decisions to grow your wealth. This comprehensive guide delves into the top investment opportunities currently available, providing insights into each sector’s potential and risks.
Key Takeaways
- Diversify Your Portfolio: Spread investments across different sectors to mitigate risk.
- Stay Informed: Regularly review market trends and adjust your investments accordingly.
- Align Investments with Goals: Ensure your investment choices align with your financial objectives and risk appetite.
- Consider Professional Advice: Consult with financial advisors to tailor an investment strategy suited to your needs.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Technology Stocks
The AI and technology sectors continue to be at the forefront of innovation and growth. Companies specializing in AI, machine learning, and automation are experiencing significant advancements, making them attractive investment options.
- Why Invest? AI is revolutionizing industries such as healthcare, finance, and manufacturing, leading to increased demand for AI-driven solutions.
- Top Picks: Companies like Nvidia, Alphabet (Google), and Microsoft are leading the charge in AI development.
Why Invest in AI and Tech Stocks?

Artificial Intelligence is transforming industries at a rapid pace—driving innovations in healthcare, finance, logistics, cybersecurity, e-commerce, and more. The adoption of AI, machine learning, and automation tools has led to explosive growth for many tech companies, making this one of the most promising sectors for investors.
Technology stocks, particularly those involved in AI development or infrastructure (like semiconductors, cloud computing, and big data), offer high growth potential and significant long-term upside.
🔍 Current Market Trends in 2025
- Generative AI boom: Following tools like ChatGPT, companies are racing to integrate AI into their workflows.
- Chipmakers thrive: Demand for advanced processors and GPUs has surged due to AI model training needs.
- Enterprise AI adoption: Corporations are increasingly investing in AI to optimize operations.
- AI in healthcare: Personalized medicine, diagnostics, and robotic surgeries are gaining traction.
- AI Regulation & Ethics: Governments are beginning to regulate AI, introducing both risks and safeguards for long-term growth.
✅ Benefits of Investing in AI & Tech
- High Growth Potential: Early investors in transformative tech often see significant returns.
- Innovation Leadership: Tech companies often set market trends and drive the economy.
- Scalability: Software-based businesses can scale globally with minimal marginal cost.
- Global Demand: AI is a global movement, not limited to one region or industry.
⚠️ Risks to Consider
- High Volatility: Tech stocks can be more volatile than traditional sectors.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments are still developing laws to govern AI usage.
- Overvaluation: Some AI-related stocks may be overhyped and priced above fundamentals.
- Technological Shifts: Rapid innovation can make some technologies (or companies) obsolete.
🏆 Top AI & Tech Stocks to Watch in 2025
Here are some notable companies actively developing or enabling AI technologies:
1. Nvidia (NVDA)
- Industry leader in GPUs critical for AI processing.
- Strong performance from data centers and AI model training support.
2. Alphabet Inc. (GOOGL)
- Parent of Google, heavily investing in AI (Google Bard, DeepMind, etc.)
- Owns key AI infrastructure and vast user data sets.
3. Microsoft (MSFT)
- Partnered with OpenAI, integrating AI into its products like Office 365, Azure, and GitHub.
- Cloud and enterprise integration of AI drives future earnings.
4. Amazon (AMZN)
- AI powers AWS, Alexa, and its logistics systems.
- Heavy investment in machine learning and generative AI infrastructure.
5. Palantir Technologies (PLTR)
- Provides data analytics and AI tools for governments and enterprises.
- Strong growth in commercial AI offerings.
6. ASML Holding (ASML)
- Not AI directly, but produces the extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography machines needed to create high-end chips used in AI applications.
7. Adobe (ADBE)
- Leader in creative software, now integrating AI tools like Firefly across its suite.
💡 Pro Tips for Investing in AI and Tech
- Diversify within tech: Don’t put all your funds into one company—use ETFs if needed.
- Watch earnings and revenue growth: Focus on companies with sustainable AI monetization.
- Evaluate partnerships and patents: Look for companies building moats with innovation.
- Stay updated on regulations: Track developments in AI ethics and data privacy laws.
Green Energy and Renewable Resources
With the global shift towards sustainability, investing in green energy has become not only a responsible choice but also a profitable one.
- Why Invest? Governments worldwide are offering incentives for renewable energy projects, and the demand for clean energy solutions is rising.
- Top Picks: Solar energy firms, wind turbine manufacturers, and companies involved in battery storage technologies are poised for growth.
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
REITs offer a way to invest in real estate without the need to own physical properties, providing exposure to the real estate market with added liquidity.
- Why Invest? REITs often provide attractive dividend yields and can serve as a hedge against inflation.
- Top Picks: Commercial and residential REITs in growing urban areas are showing strong performance.
Dividend-Paying Stocks
For investors seeking regular income, dividend-paying stocks remain a reliable option.
- Why Invest? These stocks provide steady cash flow and tend to be less volatile, making them suitable for conservative investors.
- Top Picks: Established companies in sectors like utilities, consumer staples, and telecommunications are known for consistent dividend payouts.
What Are Emerging Markets?
Emerging markets are countries transitioning from developing to developed status, characterized by rapid economic growth, industrialization, improving infrastructure, and increasing foreign investment. Examples include India, Brazil, Indonesia, Vietnam, and parts of Africa and Eastern Europe.
Investing in these markets offers a chance to participate in fast-growing economies that may outperform developed markets over the long term.
✅ Why Invest in Emerging Markets?
1. High Growth Potential
Emerging economies often grow faster than developed ones. Expanding middle classes, urbanization, and digitization drive demand for consumer goods, technology, and services.
2. Demographic Advantages
Many emerging countries have younger populations, which can translate to higher labor productivity and long-term economic expansion.
3. Undervalued Assets
Stocks and bonds in these regions are often priced lower relative to their earnings and growth potential, offering attractive valuations.
4. Diversification
Emerging market investments can reduce portfolio concentration in U.S. or European markets, offering exposure to different economic cycles and currencies.
⚠️ Risks of Investing in Emerging Markets
- Political Instability: Governments may change quickly, affecting business environments and regulation.
- Currency Risk: Foreign exchange volatility can significantly impact returns.
- Less Regulation: Corporate governance and transparency may lag behind developed markets.
- Geopolitical Tension: Conflicts, sanctions, or trade disputes can negatively affect local economies.
- Liquidity Risk: Some emerging markets may have limited access to capital markets and lower trading volumes.
🌎 Top Emerging Markets to Watch in 2025
1. India 🇮🇳
- Why: Fastest-growing major economy, strong tech and consumer sectors, government reform push.
- Key Sectors: IT, fintech, renewable energy, infrastructure.
2. Vietnam 🇻🇳
- Why: Manufacturing hub, strong exports, investor-friendly environment.
- Key Sectors: Textiles, electronics, logistics, agriculture.
3. Indonesia 🇮🇩
- Why: Resource-rich, large population, digital adoption.
- Key Sectors: E-commerce, fintech, commodities, energy.
4. Brazil 🇧🇷
- Why: Agricultural and natural resources powerhouse.
- Key Sectors: Mining, energy, agtech, digital banking.
5. South Africa 🇿🇦
- Why: Gateway to Africa, strong financial services, diversified economy.
- Key Sectors: Mining, telecom, consumer goods, fintech.
6. Mexico 🇲🇽
- Why: Strong ties to the U.S., manufacturing growth, supply chain realignment.
- Key Sectors: Automotive, manufacturing, retail.
📊 Best Ways to Invest in Emerging Marke
1. Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
Easy and diversified exposure to emerging economies.
- VWO – Vanguard FTSE Emerging Markets ETF
- EEM – iShares MSCI Emerging Markets ETF
- EMQQ – Emerging Markets Internet & E-Commerce ETF
- FM – iShares Frontier and Select EM ETF (for frontier markets like Nigeria, Bangladesh)
2. Mutual Funds
Actively managed funds may outperform in markets where information is harder to obtain.
3. ADR Stocks (American Depositary Receipts)
Invest in emerging market companies listed on U.S. exchanges.
4. Direct Investment
For experienced investors: buying local equities, real estate, or starting businesses in emerging markets (note: higher risk and requires in-depth knowledge).
🔍 Key Growth Sectors in Emerging Markets
| Sector | Why It’s Growing |
|---|---|
| Fintech | Mobile banking adoption in underbanked regions |
| Consumer Goods | Rising middle-class spending |
| E-commerce | Digital transformation and internet access |
| Infrastructure | Urban development and foreign investment |
| Green Energy | Government clean energy targets and funding |
| Healthcare | Growing demand for accessible medical services |
💡 Tips for Investing in Emerging Markets
- Start with ETFs or mutual funds for diversification and lower risk.
- Monitor macroeconomic indicators like GDP growth, inflation, and interest rates.
- Hedge currency exposure if investing directly in local equities or bonds.
- Think long-term: EM investments are volatile but tend to pay off over 5–10 years.
- Research local politics and policies: Understand how regulation and governance could affect business.
Investing in emerging markets can offer high growth potential, albeit with increased risk.
- Why Invest? Countries in Asia, Africa, and Latin America are experiencing rapid economic growth, presenting opportunities in infrastructure, technology, and consumer goods.
- Top Picks: Companies operating in sectors like fintech, e-commerce, and renewable energy in these regions are gaining traction.
Healthcare and Biotechnology

The healthcare sector, particularly biotechnology, continues to be a promising area for investment.
- Why Invest? Advancements in medical research and an aging global population are driving demand for healthcare services and products.
- Top Picks: Biotech firms involved in gene therapy, personalized medicine, and innovative treatments are at the forefront of this growth.
| ETF Name | Focus Area | Ticker |
|---|---|---|
| iShares Biotechnology ETF | Large & mid-cap biotech | IBB |
| SPDR S&P Biotech ETF | Equal-weighted biotech exposure | XBI |
| Health Care Select Sector SPDR Fund | Diversified healthcare | XLV |
| ARK Genomic Revolution ETF | Genomics, gene editing, biotech innovation | ARKG |
Precious Metals and Commodities
Gold, silver, and other precious metals are traditional safe-haven assets that can protect against economic downturns.
- Why Invest? These assets often retain value during periods of market volatility and inflation.
- Top Picks: Gold ETFs, silver mining companies, and commodity-focused mutual funds are popular choices among investors.
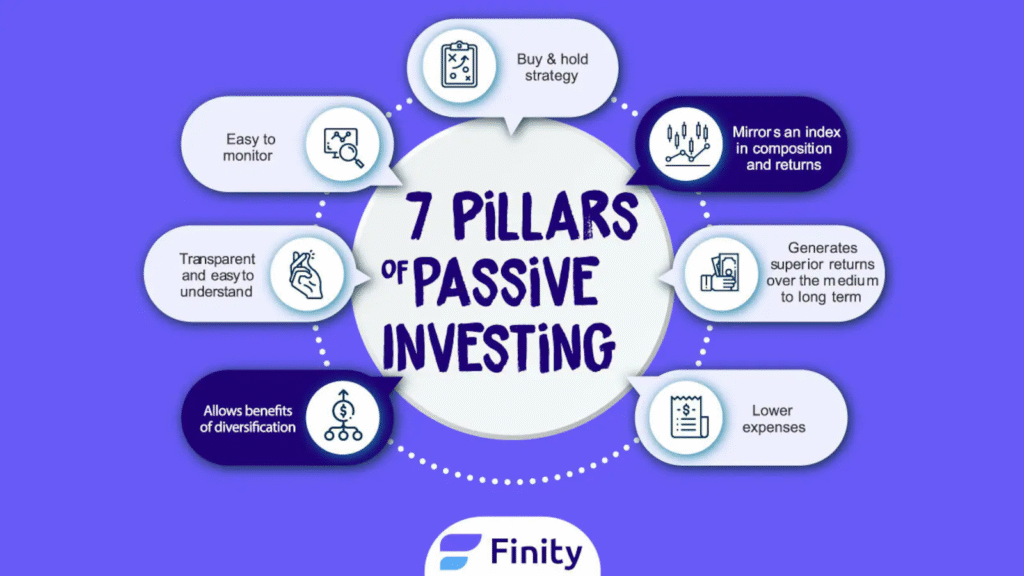
Also Read :- Is Passive Investing the Best Strategy for Long-Term Wealth Building?
Conclusion
The investment opportunities in 2025 are diverse, offering avenues for growth across various sectors. By understanding each sector’s dynamics and aligning them with your financial goals and risk tolerance, you can make informed decisions to enhance your investment portfolio. Remember, diversification is key to managing risk and achieving long-term financial success.
FAQs
1. What is the best investment for beginners?
For beginners, a diversified portfolio that includes index funds, blue-chip stocks, and REITs can provide a balanced approach to investing.
2. How can I invest in AI companies?
You can invest in AI companies through individual stocks, ETFs focused on technology, or mutual funds that include AI as part of their portfolio.
3. Are REITs a good investment in 2025?
Yes, REITs continue to offer attractive dividend yields and can provide exposure to the real estate market without the need to own physical properties.
4. What are the risks of investing in emerging markets?
Emerging markets can be volatile due to factors like political instability, currency fluctuations, and less developed regulatory environments.
5. How can I invest in renewable energy?
You can invest in renewable energy through stocks of companies in the sector, ETFs that focus on clean energy, or mutual funds with a sustainable investment mandate.
6. What are the benefits of investing in dividend-paying stocks?
Dividend-paying stocks provide regular income and tend to be less volatile, making them suitable for conservative investors seeking steady cash flow.
7. How do precious metals act as a hedge against inflation?
Precious metals like gold and silver often retain or increase in value during periods of inflation, providing a store of value when fiat currencies decline.