What Is a Personal Loan And How Does It Work?
Introduction
In today’s financial landscape, personal loans have become an increasingly popular way for individuals to meet financial needs — whether it’s consolidating debt, covering unexpected expenses, financing a wedding, or even funding a vacation. But what exactly is a personal loan, and how does it work?
This article will dive deep into the mechanics of personal loans — from the basics to more nuanced insights — to help you decide if it’s the right financial solution for your situation.
Key Takeaways:-
1. Flexible Loan Option
Personal loans are versatile and can be used for a wide range of purposes, including debt consolidation, home improvements, medical expenses, weddings, and vacations.
2. Secured vs. Unsecured
Personal loans can be secured (backed by assets like a car or house) or unsecured (not requiring collateral). Unsecured loans are more common, but they typically come with higher interest rates.
3. Fixed or Variable Interest Rates
Personal loans often have fixed interest rates, meaning your monthly payment stays the same throughout the loan term. However, some loans have variable rates that can change over time.
4. Credit Score Affects Approval and Rates
Your credit score plays a significant role in determining whether you qualify for a loan and what rate you’ll receive. Higher scores typically result in better terms.
5. Loan Terms and Repayment
Personal loans are generally short-term (2-7 years) and repaid in fixed monthly installments. A longer term can lower monthly payments, but you’ll pay more in interest over time.
6. Compare Lenders Before Committing
Interest rates, fees, loan terms, and eligibility criteria can vary greatly among lenders. It’s essential to shop around to find the best deal for your situation.
7. Timely Repayment Improves Credit Score
Making regular, on-time payments can improve your credit score, demonstrating your ability to manage debt responsibly.
8. Risks of Defaulting
If you fail to make payments, the lender may charge late fees, report missed payments to the credit bureaus, or in the case of secured loans, seize the collateral. Defaulting can severely impact your credit score.
9. Consider Alternatives
Before taking out a personal loan, consider alternatives such as credit cards, home equity loans, or lines of credit. These may offer better terms depending on your financial situation.
10. Responsible Borrowing is Key
Only take out a personal loan if you genuinely need it, and make sure you can comfortably meet the monthly payments without compromising your financial health.
What Is a Personal Loan?

A personal loan is a type of installment loan offered by banks, credit unions, and online lenders that allows individuals to borrow a fixed amount of money. Unlike a credit card, which offers a revolving line of credit, a personal loan provides a lump sum that is repaid over a set period of time, typically in monthly installments.
The borrowed amount, known as the principal, is repaid with interest, and the interest rate can be fixed or variable depending on the lender and your creditworthiness.
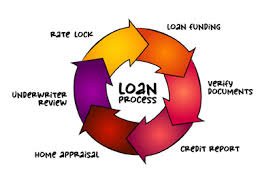
How Do Personal Loans Work?
When you apply for a personal loan, the lender evaluates your credit history, income, employment, and other financial factors to determine whether you qualify and what interest rate you’ll be offered.
Key steps:
- Application – Submit personal and financial information.
- Approval – Lenders assess credit score, income, debt-to-income ratio.
- Loan Terms – If approved, terms like loan amount, interest rate, and repayment schedule are presented.
- Funding – Funds are typically deposited directly into your bank account.
- Repayment – Monthly payments begin, consisting of principal and interest.
Types of Personal Loans
Not all personal loans are the same. They are often categorized based on their purpose, collateral, or repayment terms.
Common types include:
- Debt Consolidation Loans
- Medical Loans
- Wedding Loans
- Vacation Loans
- Home Improvement Loans
- Emergency Loans
- Moving Loans
Each serves a different financial goal, but the structure remains consistent: lump-sum funding and fixed repayments.
Secured vs. Unsecured Personal Loans
What Is a Secured Personal Loan?
A secured personal loan is a type of loan where you borrow money and offer an asset, such as a car, house, or savings account, as collateral. If you fail to repay the loan, the lender has the legal right to seize the collateral to recover their money.
Key Features of Secured Personal Loans:
- Collateral Required: Assets such as real estate, cars, or savings accounts are typically used as collateral.
- Lower Interest Rates: Because the loan is backed by an asset, the lender’s risk is reduced, resulting in lower interest rates compared to unsecured loans.
- Higher Loan Amounts: Secured loans may allow for larger loan amounts since the lender has the added security of collateral.
- Longer Terms: Secured loans often have longer repayment terms, giving you more time to pay back the debt.
Pros of Secured Personal Loans:
- Lower Interest Rates: Collateral reduces the lender’s risk, which can result in lower rates for the borrower.
- Higher Borrowing Limits: Lenders may be more willing to approve larger loans since there is collateral involved.
- Easier Approval: Borrowers with poor credit may find it easier to get approved for a secured loan because the lender has the option to recover their funds if you default.
Cons of Secured Personal Loans:
- Risk of Losing Collateral: If you fail to repay the loan, the lender can seize your collateral, such as your house or car.
- Longer Loan Terms Can Be Risky: While longer terms can lower monthly payments, they may lead to paying more in interest over time.
2. What Is an Unsecured Personal Loan?
An unsecured personal loan does not require collateral. Instead, the lender will rely on your creditworthiness, which is typically determined by your credit score, income, employment status, and debt-to-income ratio. Since there is no collateral, these loans tend to be riskier for lenders, which often results in higher interest rates.
Key Features of Unsecured Personal Loans:
- No Collateral Needed: No asset is required as collateral, which means there is no risk of losing property if you default.
- Higher Interest Rates: Because the lender is taking on more risk, they typically charge higher interest rates than secured loans.
- Lower Loan Amounts: Since there’s no collateral, the amount you can borrow may be lower compared to a secured loan.
- Shorter Loan Terms: Unsecured loans generally have shorter repayment terms, which means higher monthly payments but a shorter total repayment period.
Pros of Unsecured Personal Loans:
- No Risk of Losing Assets: There’s no collateral, so your property (such as your home or car) is not at risk if you can’t make payments.
- Faster Approval: Without the need for appraising or securing collateral, the approval process may be quicker.
- Ideal for Borrowers Without Valuable Assets: If you don’t own valuable assets, an unsecured loan is your best option.
Cons of Unsecured Personal Loans:
- Higher Interest Rates: Since there’s no collateral to fall back on, lenders charge higher interest rates, especially for borrowers with lower credit scores.
- Strict Eligibility Requirements: Lenders may require good credit and stable income to approve your application.
- Smaller Loan Amounts: You may be limited in how much you can borrow compared to a secured loan.
Key Differences Between Secured and Unsecured Loans
| Feature | Secured Personal Loan | Unsecured Personal Loan |
|---|---|---|
| Collateral | Required (e.g., home, car, savings) | Not required |
| Interest Rates | Typically lower | Typically higher |
| Loan Amount | Can be higher, depending on collateral | Usually lower due to higher risk for lender |
| Loan Term | Often longer | Usually shorter |
| Approval Requirements | Easier for borrowers with bad credit | Stricter approval based on creditworthiness |
| Risk | Risk of losing collateral if you default | No risk of losing property, but may impact credit score if you default |
When to Choose a Secured Loan
Opting for a secured loan might be ideal if:
- You have valuable assets you can use as collateral, such as a home or car.
- You need to borrow a large sum of money.
- You have a poor credit score and need a way to improve your approval chances.
- You want to lock in lower interest rates.
Example Scenarios for Secured Loans:
- Home Equity Loans: If you need funds for home improvements, you may use the equity in your home as collateral.
- Auto Loans: A car loan where the car itself acts as collateral.
When to Choose an Unsecured Lo
Opt for an unsecured loan if:
- You don’t have valuable assets to offer as collateral.
- You prefer the flexibility of not risking your property.
- You want a quicker approval process, and you have a strong credit history.
- You need a smaller amount of money or are focused on paying off existing debts without providing collateral.
Example Scenarios for Unsecured Loans:
- Debt Consolidation Loans: If you want to consolidate credit card debt but don’t want to risk your home or other assets.
- Personal Expenses: Emergencies, weddings, or vacations where you don’t want to risk personal property.
Unsecured Personal Loans
- No collateral required
- Based on creditworthiness
- Higher interest rates (in some cases)
Secured Personal Loans
- Backed by assets (e.g., car, savings)
- Lower interest rates
- Higher risk: defaulting means losing the asset
Common Uses of Personal Loans
Personal loans are incredibly versatile, making them one of the most popular forms of consumer financing. Here are the most common ways people use personal loans:
1. Debt Consolidation
One of the top reasons people take out personal loans is to consolidate high-interest debts—especially credit card balances—into a single, lower-interest monthly payment. This can:
- Simplify repayment
- Reduce the overall interest paid
- Improve your credit score if used responsibly
2. Medical Expenses
Unexpected medical bills can be overwhelming. Personal loans can help cover:
- Hospital stays
- Surgery
- Dental work
- Other out-of-pocket medical costs
This is especially helpful if you’re uninsured or your insurance doesn’t fully cover the expense.
3. Home Renovation or Repairs
Many homeowners use personal loans to fund:
- Kitchen or bathroom remodels
- Roof or window replacements
- Emergency repairs (e.g., plumbing, HVAC)
Unlike home equity loans, personal loans don’t require using your home as collateral.
4. Major Life Events
Life is full of big moments—and expenses. People often use personal loans for:
- Weddings
- Honeymoons
- Births
- Funerals
- Milestone celebrations
These one-time events can be costly, and a loan may help manage costs without draining savings.
5. Education Expenses
Although federal student loans are often the best choice for tuition, personal loans are sometimes used to:
- Cover private education costs
- Pay for certifications or training programs
- Handle school-related expenses not covered by other loans
6. Moving Costs
Relocation isn’t cheap—especially if you’re moving cross-country or relocating for a new job. A personal loan can help cover:
- Truck rental and movers
- Utility deposits
- Temporary housing
- Travel expenses
7. Starting or Growing a Business
While small business loans are designed for entrepreneurs, personal loans can also be used to:
- Launch a side hustle
- Buy equipment
- Cover initial costs before securing business funding
This is common among freelancers or home-based businesses.
8. Vacation or Travel
While not financially ideal for everyone, some use personal loans to fund major vacations like:
- Honeymoons
- International trips
- Bucket list experiences
It’s important to balance this with your long-term financial goals.
9. Vehicle Purchase or Repairs
Personal loans can be used to:
- Buy a used car from a private seller
- Cover down payments
- Pay for major car repairs
They are especially useful if you don’t qualify for a traditional auto loan.
10. Emergencies
Life is unpredictable. Personal loans offer quick cash to deal with:
Pet medical bills
Job loss
Natural disasters
Urgent family needs
While personal loans can be useful, they should be used responsibly and only when necessary.
The Loan Application Process
Here’s what you can expect:
- Research and compare lenders
- Check your credit score
- Get prequalified (optional)
- Submit a formal application
- Upload required documents (proof of ID, income, address)
- Wait for approval
- Accept the terms and receive funds
Personal Loan Eligibility Criteria

Eligibility varies by lender, but generally, you’ll need:
- Minimum credit score (typically 600+)
- Proof of income (pay stubs, tax returns)
- Debt-to-income ratio below 40%
- U.S. citizenship or legal residency
- Valid bank account
Some lenders may cater to borrowers with bad credit, but interest rates will be higher.
How Interest Rates Are Determined
Interest rates depend on several factors:
- Credit score – Higher scores = lower rates
- Loan term – Shorter terms often have lower rates
- Income and employment status
- Debt-to-income ratio
- Lender’s policies
Rates can range from 5% to 36%, and it’s vital to compare offers before accepting a loan.
Pros and Cons of Personal Loans
Pros
- Fixed repayment schedule
- No collateral needed (unsecured)
- Quick access to funds
- Can improve credit score with timely payments
- Useful for debt consolidation
Cons
- High interest for low credit scores
- Fees (origination, late payment, prepayment penalties)
- Risk of default and credit damage
- Temptation to borrow unnecessarily
Tips for Managing Personal Loan Repayment
Set Up Automatic Payments
Most lenders offer auto-debit options from your bank account.
Benefits:
Avoid missed or late payments
May qualify for small interest rate discounts (e.g., 0.25%)
Pro tip: Make sure your account has sufficient funds to prevent overdraft fees.
Create a Dedicated Budget
Include your loan repayment as a fixed monthly expense.
Prioritize your loan payment above discretionary spending.
Use budgeting apps like Mint, YNAB, or Goodbudget to track expenses.
Pay More Than the Minimum (If Possible)
Extra payments help reduce the principal faster.
You’ll save on interest and may repay the loan months ahead of schedule.
Check if your lender charges prepayment penalties first.
Schedule Reminders
If you don’t use autopay, set calendar reminders for due dates.
You can also enable SMS/email alerts from your lender’s app or portal.
Keep All Loan Documents Organized
Save your loan agreement, payment schedule, and contact information for the lender.
These are helpful if disputes or questions arise later.
Refinance if You Qualify for Better Terms
If your credit score improves, you might qualify for a lower interest rate.
Refinancing can reduce monthly payments or shorten your loan term.
Always calculate the total cost (fees, new term) to ensure it’s worth it.
Avoid Taking on New Debt
Don’t add new credit cards or loans while repaying your current one.
It could strain your budget and lower your credit score.
Communicate With Your Lender If You Face Financial Trouble
Many lenders offer hardship plans, deferments, or payment pauses.
Contact them early—before missing a payment.
Monitor Your Credit Score
On-time payments improve your credit score.
Use tools like Credit Karma, Experian, or your bank’s free monitoring services.
Celebrate Milestones
Reward yourself (within budget!) after paying off a percentage of your Personal loan.
This keeps you motivated and reinforces good habits.
Also Read:-Top 5 Benefits Of Getting A Personal Loan In 2025
Conclusion
Personal loans can be a powerful tool when used correctly. They offer a structured, often more affordable alternative to credit cards for funding everything from emergencies to major life milestones. However, they’re not without risk.
FAQs
1. Can I get a personal loan with bad credit?
Yes, some lenders specialize in bad credit loans, but interest rates will likely be higher.
2. What’s the average interest rate on a personal loan?
As of 2025, it typically ranges between 6% and 36% depending on creditworthiness and lender.
3. How fast can I get a personal loan?
Some online lenders offer same-day funding, while traditional banks may take a few days.
4. Do personal loans affect my credit score?
Yes. A hard inquiry can lower your score slightly, but timely payments can boost it over time.
5. Can I repay a personal loan early?
Usually yes, but some lenders charge a prepayment penalty, so check the terms.
6. What’s the difference between a personal loan and a line of credit?
A personal loan is a one-time lump sum; a line of credit is a revolving credit you can draw from multiple times.
7. Is a personal loan better than a credit card for large expenses?
Yes, in most cases. Personal loans often have lower interest rates and structured payments, making them ideal for larger expenses.
Before taking out a personal loan, it’s important to assess your financial situation, compare lenders, read the fine print, and make sure repayment fits into your budget.
When used responsibly, personal loans can help you bridge financial gaps, manage debt more effectively, and even improve your credit score.